Chapter 6 Analysis of a Malware Specimen
| Environment Baseline |
| Host Integrity Monitors |
| Name: ESET SysInspector | |
| Page Reference: 367 |
|
| Author/Distributor: ESET |
|
| Available From: http://www.eset.com/us/download/free-antivirus-utilities; http://download.eset.com/download/sysinspector/32/ENU/SysInspector.exe |
|
| Description: ESET SysInspector is a graphical Windows diagnostic tool that takes a “snapshot” of the system state of a target computer, including running processes, Registry, network connections, and startup contents. Once a snapshot has been taken, ESET applies heuristics to assign a “risk level” for each item logged allowing the digital investigator to conduct a number of analytical processes, including log generation, log comparison (diffing), and filtering based upon risk color-coding. |
 |
|
| Name: FingerPrint v2.1.3 |
| Page Reference: 367 |
| Author/Distributor: 2BrightSparks |
| Available From: http://www.2brightsparks.com/assets/software/FingerPrint_Setup.zip |
| Description: A lightweight GUI-based utility that monitors files and directories for modifications and deletions. |
| Name: Regshot |
| Page Reference: 367 |
| Author/Distributor: TiANWEi |
| Available From: http://sourceforge.net/projects/regshot |
| Description: A free and open source Registry comparison tool that allows the user to take a snapshot of the Registry prior to the execution of a program, and a second snapshot after execution. Using the compare feature, RegShot provides the digital investigator with a report detailing the differences in the Registry as a result of executing the program. |
| Name: Winalysis |
| Page Reference: 367 |
| Author/Distributor: Winalysis Software |
| Available From: <This URL has been removed as it was flagged as malicious by Google Safe Browsing> |
| Description: A favorite of digital investigators, Winalysis is a program that enables the user to save a snapshot of a subject system’s configuration and then monitor for changes to files, the Registry, users, local and global groups, rights policy, services, the scheduler, volumes, shares resulting from software installation, or unauthorized access. |
 |
| Installation Monitors |
| Name: InCntrl5 |
| Page Reference: 368 |
| Author/Distributor: PC Magazine |
| Available From: http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,1759,9882,00.asp |
| Description: A favorite of many digital investigators, InCtrl5 monitors the changes made to the host system as a result of installing software. InCtrl5 offers an intuitive GUI and Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) reporting. |
| Name: InstallSpy |
| Page Reference: 368 |
| Author/Distributor: 2BrightSparks |
| Available From:http://www.2brightsparks.com/assets/software/InstallSpy_Setup.zip |
| Description: A utility enabling the user to track any changes to the Registry and file system when a program is executed, installed, or uninstalled. |
| Name: InstallWatch |
| Page Reference: 368 |
| Author/Distributor: Epsilon Squared |
| Available From: http://web.archive.org/web/20090216115249/http://www.epsilonsquared.com/ |
| Description: Software utility developed by Epsilon Squared, Inc., that records modifications made to a subject system during the installation of software, or as a result of hardware and configuration changes. |
| Name: SysAnalyzer |
| Page Reference: 368 |
| Author/Distributor: Verisgn iDefense Labs |
| Available From: http://sandsprite.com/blogs/index.php?uid=7&pid=185 |
| Description: An automated malicious code runtime analysis application, SysAnalyzer enables the digital investigator to execute an unknown binary, and then monitors various aspects of the host system, including running processes, open ports, loaded drivers, injected libraries, file modifications, Registry changes, API calls made by the target process, and certain network traffic (HTTP; IRC; and DNS). SysAnalyzer quickly builds an intuitive report identifying the changes made as a result of execution of the program on the host system. |
 |
| Environment Emulation |
| Name: Internet Services Simulation Suite (INetSIM) |
| Page Reference: 388 |
| Author/Distributor: Thomas Hungenberg and Matthias Eckert |
| Available From: http://www.inetsim.org/ |
| Description: For use on Linux and FreeBSD/OpenBSD systems. INetSIM is a software suite for simulating common Internet services in a laboratory environment. Specifically developed to assist in the analysis of network behavior of unknown malware specimens, INetSIM provides the digital investigator with a common control and logging platform for environment adjustment during dynamic analysis. |
| Name: SimpleDNS |
| Page Reference: 388 |
| Author/Distributor: JH Software |
| Available From: http://www.simpledns.com/ |
| Description: A lightweight and intutive DNS server with a GUI front-end. DNS emulation and adjustment within the digital investigator’s laboratory environment can be configured quickly and easily using the Quick Zone Wizard feature, shown in the following digram. |
 |
| Dynamic Analysis —Active System and Network Monitoring |
| Process Monitoring |
| Name: CurrProcess |
| Page Reference: 372 |
| Author/Distributor: Nir Sofer/NirSoft |
| Available From: http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/cprocess.html |
| Description: A GUI and command-line utility, CurrProcess displays a list of all processes running on a target system. By selecting a target process, CurrProcess displays PE version information (from the PE resources) and details relating to modules loaded into memory associated with process image. The memory of a target process can be dumped to a text file using the toolbar button or by pressing Ctrl+M, and details associated with the process can be quickly copied to the clipboard by right-clicking the target process and selecting “Copy Selected Processes” from the menu. |
| Name: Explorer Suite |
| Page Reference: 372 |
| Author/Distributor: Daniel Pisteli/NTCore |
| Available From: http://www.ntcore.com/exsuite.php |
| Description: A freeware suite of tools developed by Daniel Pisteli, Explorer Suite comes with a series of tools to assist the digital investigator in conducting malware forensics, including a rich PE Viewer (CFF Explorer), a packing detection framework (PE Detective/Signature Explorer), and a process viewer (Task Explorer). Task Explorer is a dual-paned graphical process analysis tool. The top pane reveals the running processes along with respective PIDS, system paths, and PE version information; the lower pain displayes modules loaded into memory by a selected process. Right clicking on a target process provides the digital investigator with a shell context menu of additional options, including PE dumping and analysis in CFF Explorer. |
 |
| Name: Mitec Process Viewer |
| Page Reference: 372 |
| Author/Distributor: Michael Mutl/MiTeC |
| Available From: http://www.mitec.cz/Downloads/PV.zip |
| Description: A lightweight graphical process analysis utility, the Process Viewer interface provides distinct tabs for isolated analysis of processes, drivers, and services. Upon selecting a target process, the “details” button provides an additional analysis interface enabling the digital investigator to drill down into the handles, performance, loaded modules, threads, and child processes, among other details, associated with the process. |
| Name: Process Hacker |
| Page Reference: 372 |
| Author/Distributor: wj32 |
| Available From: http://processhacker.sourceforge.net/ and http://sourceforge.net/projects/processhacker/ |
| Description: A robust graphical process analsysis tool, Process Hacker gives granular visibility into running processes, services, and network activity. Right-clicking on process offers additional analytical options including threads, handles, process memory, and environment details. |
 |
| File System Monitoring |
| Name: ProcessActivityView |
| Page Reference: 372 |
| Author/Distributor: Nir Sofer/NirSoft |
| Available From: http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/process_activity_view.html |
| Description: A useful tool for monitoring file system interaction by a target process, ProcessActivityView displays the system path and files accessed by the process, associated statistics, and the module in memory responsible for accessing the file. Right-clicking on a target file system artifact presents the digital investigator with a shell context menu of additional analytical options, as displayed in the following diagram. |
 |
| Name: DirMon (included in GiPo@FileUtilities) |
| Page Reference: 373 |
| Author/Distributor: Gibin Software House |
| Available From: http://www.gibinsoft.net/ |
| Description: DirMon provides the digital investigator with a practical and simple way to track changes in a target directory. After configuring the granularity of monitoring, DirMon provides real-time insight into changes made to the directory, including an event listing and statistical ticker. Analytical results are saved and compiled into an HTML report. |
 |
| Name: FileMon |
| Page Reference: 372 |
| Author/Distributor: Mark Russinovich and Bryce Cogswell (Sysinternals)/Microsoft |
| Available From: http://web.archive.org/web/20090801183050/http://technet.microsoft.com/en- us/sysinternals/bb896642.aspx |
| Description: A legacy tool discontued by Microsoft (and replaced with Process Monitor), FileMon is a powerful GUI-based file-monitoring utility that reveals the files and .dlls opened, read, or deleted by each running process as well as a status column, which advises of the failure or success of the monitored activity. FileMon also provides the investigator with filter options, a search function, and the ability to save the results to a file for offline analysis. Identified artifacts of interest can quickly be accessed on the file system by double-clicking on a target entry in the user interface. Although obsolete and unavailable for download from Microsoft, the utility is still a favorite among digital investigators and available from Web archives on Archive.org. |
 |
| Name: Tiny Watcher |
| Page Reference: 373 |
| Author/Distributor: Olivier Lombart |
| Available From: http://kubicle.dcmembers.com/watcher/ |
| Description: A graphical file, directory, and registry monitoring tool, Tiny Watcher takes a baseline snapshop of the subject system state and then makes notifications when a change is detected on the system. For example, in the following figure, Tiny Watcher captured the invocation of a new process, the system path to the suspect executable (winhelp.exe), and the resulting system changes. |
 |
| Registry Monitoring |
| Name: RegMon |
| Page Reference: 374 |
| Author/Distributor: Mark Russinovich and Bryce Cogswell (Sysinternals)/Microsoft |
| Available From: http://web.archive.org/web/20090627020908/http://technet.microsoft.com/en- us/sysinternals/bb896652.aspx |
| Description: A legacy tool discontinued by Microsoft (and replaced with Process Monitor), RegMon actively reveals which processes are accessing the host system’s Registry, keys, and the Registry data that is being read or written. The tools includes a filter function and can either provide time stamps for captured events, or simply show the amount of time that has elapsed since the last time the event window was cleared. Unlike static Registry analysis tools, the advantage of using RegMon during dynamic analysis of a malicious code specimen is that it provides the digital investigator with the ability to trace how programs are interacting with the Registry in real time. Although obsolete and unavailable for download from Microsoft, the utility is still available from Web archives on Archive.org. |
 |
| Autostart Monitoring |
| Name: Autoruns |
| Page Reference: 375 |
| Author/Distributor: Mark Russinovich and Bryce Cogswell (Sysinternals)/Microsoft |
| Available From: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb963902 |
| Description: Autoruns is a program that can run against a live system or a forensic duplicate to extract details from various locations that will launch programs when a Windows computer starts up. In addition to providing a categorized interface to this information, Autoruns can be useful for identifying unusual startup entries. For example, Autoruns can show executables that have not been signed, which may be an indication of malware. |
 |
| Name: Autostart Explorer |
| Page Reference: 375 |
| Author/Distributor: Mischel Internet Security |
| Available From: http://www.misec.net/products/autostartexplorer/ |
| Description: A triple-paned graphical autostart insepction utility, Autostart Explorer provides an expandable tree listing of Registry keys, Startup Folders, .bat, and.ini files on a target system on a left- side viewing pane. Upon selecting an item of interest, the top right pane displays all discovered autostarted files, while the bottom left pane provides a description of the selected item. |
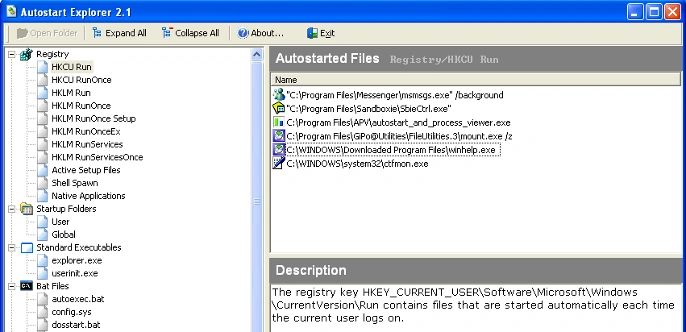 |
| Name: Autostart and Process Viewer |
| Page Reference: 375 |
| Author/Distributor: Konrad Papala Software |
| Available From: http://www.konradp.com/products/autostart-and-process-viewer/ |
| Description: Useful for quickly auditing running processes and autostart locations on a target system, Autostart and Process Viewer is a graphical utility that succinctly separates data into distinct tabs in the user interface. Once a target autostart location or process is selected, further details can be acquired using the toolbar menu options. |
 |
| Name: WhatinStartup |
| Page Reference: 375 |
| Author/Distributor: Nir Sofer/NirSoft |
| Available From: http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/what_run_in_startup.html |
| Description: The successor tool to Nirsoft’s now obsolete StartupRun utility, WhatinStartup is an ituitive graphical utility that reveals detailed information about programs identified on a target system as having a autostart mechanism. In a one-pane GUI with numerous data columns, WhatinStartup identifies a program, along with the respective autostart type (startup folder or Registry), command-line properties/system path to executable, PE version information in memory, autostart location, file system metadata (created time and modified times), file attributes, and process creation date/time. |
 |
| Network Forensics |
| Name: Capsa Network Analyzer |
| Page Reference: 376 |
| Author/Distributor: Colasoft |
| Available From: http://www.colasoft.com/capsa/ |
|
Description: Capsa is powerul and robust GUI-based network packet capture and analysis tool. The free version of the tool (Colasoft Capsa 7 Free) includes additional network forensic tools, Mac Scanner, Packet Builder, Packet Player, and Ping Tool. A great companion utility to Wireshark, in addition to full traffic capture, Capsa has predefined filters for HTTP, e-mail, DNS, FTP and Instant Messenger traffic capture; these filters are conversely available in the “Replay” analysis options of Capsa. Rich with real- time and post-processing analysis features, Capsa can be used to quickly and effectively gain visibilityinto network traffic resulting from the dynamic analysis of a malware specimen. |
 |
| Name: Network Miner |
| Page Reference: 376 |
| Author/Distributor: Erik Hjelmvik |
| Available From: http://sourceforge.net/projects/networkminer/ |
|
Description: A valuable tool for network traffic capture and analysis, Network Miner is a graphical |
 |
| Port Monitoring |
| Embedded Artifacts Revisited |
| Name: ActivePorts |
| Page Reference: 378 |
| Author/Distributor: DeviceLock |
| Available From: http://www.devicelock.com/freeware.html |
|
Description: A light-weight graphical port monitoring utility that displays process-to-port mapping, |
|
 |
| Name: CurrPorts |
| Page Reference: 378 |
| Author/Distributor: Nir Sofer/NirSoft |
| Available From: http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/cports.html |
|
Description: A flexible graphical port monitoring utility, CurrPorts offers detailed information about the |
 |
| Name: TCPView |
| Page Reference: 378 |
| Author/Distributor: Mark Russinovich (Sysinternals)/Microsoft |
| Available From: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb897437 |
| Description: A favorite GUI-based port monitoring utility of many digital investigators, TCPView displays open ports, connection, and associated process details. |
 |
| API Monitoring |
| Name: API Monitor v2 |
| Page Reference: 379 |
| Author/Distributor: Rohitab Batra |
| Available From: http://www.rohitab.com/apimonitor |
| Description: Although currently in Alpha stage of development, API Monitor v2 is a feature-rich graphical API monitoring tool that implements an eight-window “dashboard” of distinct data viewing panes: API Capture Filter, Running Processes, Hooked Processes, Summary of API Calls, Hex Buffer, Output Statistics, Call Stack, and Parameters. API Monitor v2 provides for intutive API Capture Filter options, a process monitor for selecting a target process to hook, and granularity in trace output. “Digital investigator friendly” shell context menus contain numerous shortcuts for ease of researching API calls of interest. |
 |
| Defeating Obfuscation |
| Process Memory Dumping Tools |
| Name: ProcDump |
| Page Reference: 405 |
| Author/Distributor: Mark Russinovich (Sysinternals)/Microsoft |
| Available From: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/dd996900 |
|
Description: A command-line process memory acquisition tool. |
Helpful Switches:
|
| PE Import Address Table Reconstruction |
| Name: ReVirgin |
| Page Reference: 411 |
| Author/Distributor: +Tsehp |
| Available From: Numerous underground reverse engineering sites—download with care |
|
Description: Similar to ImpREC, ReVirgin is a graphical Import Address Table (IAT) rebuilding utility, |
 |
| Disassembly Visualization |
| Name: BinNavi |
| Page Reference: 415 |
| Author/Distributor: Zynamics |
| Available From: http://www.zynamics.com/binnavi.html |
| Description: BinNavi is the de facto tool for binary code reverse engineering tools through graph visualization. Used inextricably with IDA Pro, a MySQL database, and other third-party utilities, BinNavi enables the digital investigator to import IDA database files (.idb) and navigate the disassembled code in a visually stunning graph form. Once in graph form, BinNavi offers a myriad of analytical features to view, analyze, and annotate the code of the target module (BinNavi nomenclature for a single disassembled file). In addition, using debug clients, the BinNavi debugger offers robust functionality for controlling and analyzing the execution of a target process. |
 |
| PE Resource Viewers |
| Name: Resource Hacker |
| Page Reference: 417 |
| Author/Distributor: Angus Johnson |
| Available From: http://www.angusj.com/resourcehacker/ |
| Description: An easily navigable, dual-paned graphical PE Resource analysis (and editing) tool. Resource Hacker displays available PE Resources in an expandable tree menu in the left-hand viewing pane, while selected content is displayed in the right-hand viewing pane. Resources can be extracted and saved to disk using the shell context menu or the “Action” toolbar. |
 |
| Interacting with and Manipulating the Malware Specimen |
| Prompting Trigger Events |
| Name: WinHTTrack |
| Page Reference: 425 |
| Author/Distributor: Xavier Roche |
| Available From: http://www.httrack.com |
| Description: WinHTTrack is the Windows version of the graphical Web site copying tool, HTTrack. A valuable tool for copying Web site content for offline browsing and reconstructing Web content locally, WinHTTrack offers granular configuration options for copying depth and content acquisition. |
 |
| Digital Virology |
| Context Triggered Piece-Wise Hashing and Indicators of Likeness |
| Name: SSDeep |
| Page Reference: 435 |
| Author/Distributor: Jesse Kornblum |
| Available From: http://ssdeep.sourceforge.net/ |
| Description: A fuzzy hashing tool that computes a series of randomly sized checksums for a file, allowing file association between files that are similar in file content but not identical. |
Helpful Switches:
|
| Name: Scout Sniper |
| Page Reference: 437 |
| Author/Distributor: Don C. Weber/Security Ripcord |
| Available From: http://www.cutawaysecurity.com/blog/scout-sniper |
| Description: Sniper Scout (sniperscout) is a wrapper program (.exe and Python script) for two tools that can be used during digital virology analysis—ssdeep and YARA. In particular, sniperscout can be run against a target directory of specimens using a specific YARA rule or the contents compared with contextual piecewise hashing using the Fuzzy dynamic link library (fuzzy.dll) from ssdeep (as shown in the following figure). C:\Python25>python scoutsniper.py -s c:\Malware\specimens\Crvhost.exe -d c:\Malware\specimens sdir: c:\Malware\specimens There is no warrenty for this program. User at your own risk and only with permission. If you use the deletion option you may damage your system, programs or applications. Enter YES to indicate you have read and understand this warning and with to proceed. -> YES Scout Sniper: Happy Hunting Start Time: 2011-07-10.01:59:10.546000 Searching Local: c:\Malware\specimens Sample File Hash: '49152:duXwKHOwaabc/8DCBq4QI4hSPFEK8FzVzAQ2YMgE:due/Suq4R4IElAQ29' Checking: c:\Malware\specimensavhelper Alert: avhelper scored 91 Checking: c:\Malware\specimensCrvhost.exe Alert: Crvhost.exe scored 100 Checking: c:\Malware\specimenshelpfile.exe Alert: helpfile.exe scored 96 Checking: c:\Malware\specimensupdatehelp.exe Alert: updatehelp.exe scored 96 Checking: c:\Malware\specimensWindowsUpdate.exe Alert: WindowsUpdate.exe scored 96 Checking: c:\Malware\specimenswinhelp.exe Alert: winhelp.exe scored 96 Checking: c:\Malware\specimenswinsrv.exe Alert: winsrv.exe scored 96 Checking: c:\Malware\specimensWinUpdate.exe Alert: WinUpdate.exe scored 96 Finish Time: 2011-07-10.01:59:14.750000 Scout Sniper Done |
Helpful Switches:
|
